On earth there are variety of soils and they all exhibit different kinds of behaviour.
Properties of soils vary not only with soil types but also with soil grain arrangement and moisture content in the soil.
 For example we may safely assume that gravel and sand soils will behave differently than clays, but we cannot assume or say that all sands will behave alike or all clays will behave similarly.
For example we may safely assume that gravel and sand soils will behave differently than clays, but we cannot assume or say that all sands will behave alike or all clays will behave similarly.
A loose sand will behave differently with the same sand if it is dense.
Similarly saturated clay will behave differently from the same clay in dry state.
So to understand the behviour of soil we try to evaluate its properties in terms of
- grain characteristics
- arrangement of particles
- moisture content.

Using these evaluated properties we try to classify the soil into different categories. And properties of soil that help in identification and classification of soil are called Index Properties.
Index properties can be divided into two categories
- soil grain properties
- soil aggregate properties
soil grain properties, as the name suggests, depends on individual grains of soil.
 Properties in this category are
Properties in this category are
- mineralogical composition
- specific gravity of soilds
- size and shape of grains
Most important properties of individual grains of soil are the particle size distribution and grain shape.
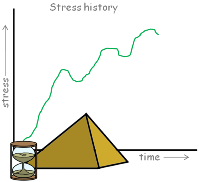
Soil aggregate properties, these are dependent on soil mass as a whole, that is a huge amount of individual grains of soil put together. This represents the collective behaviour of soil. These aggregate properties depend upon soil stress history, how the soil has formed and soil’s structure.
These properties are of greater significance in the engineering practice.